

I find it satisfying to see the graph come down :)


I find it satisfying to see the graph come down :)


Yes, sorry, there was some serious lagg in fetching posts from Lemmy World that persisted for several days and accumulated a 1-week delay.
But after upgrading Mander it is now fetching data from LW quite rapidly and it should be back in-sync in about a day and a half from now.
If you are curious about the ranking algorithm, there is some info here: https://join-lemmy.org/docs/contributors/07-ranking-algo.html


If the timing is right, I would bring a mushroom grow bag with mushrooms sprouting.
If not… probably my radiacode gamma spectrometer and some of my radioactive items. Maybe a clock with radium painted dials and a piece of trinitite. I think that there are many different points of discussion that can be of interest to a broad audience (radioactivity, spectroscopy, electronics, US labor law story of the radium girls, nuclear explosions, background radiation… etc). As a bonus I can bring a UV flash light and show the radium fluorescence. Adults love UV flash lights.


Dragonfruit lemonade (agua de pitahaya) is delicious!


First of all, congratulations for bringing a baby girl into this world!! You must be really excited! I am very happy for you!
This looks very cool. I set up a wiki (https://ibis.mander.xyz/) and I will make an effort to populate it with some Lemmy lore and interesting science/tech 😄 Hopefully I can set some time aside and help with a tiny bit of code too.


Thank you for the positivity 💚 I wholeheartedly agree!
Drama and negativity drives engagement, and this form of engagement can easily trigger a feedback loop in which negativity keeps piling on and voices of support are practically muted.
We are participating in an open source project that has some very ambitious goals. Things can be messy, mistakes happen, there are risks, and people have many different opinions and moods. Heated discussions can be a healthy part of the process. But, once the dust is allowed to settle for a bit, it is good to remember that we are humans and that we are here because we have some shared goals.
I think the majority of people around here are kind and have a positive outlook, but perhaps it is more motivating to speak out when we have negative comments than positive ones. So, thank you for taking the time to write this positive message!


I am also quite interested in this. It is not something that keeps me awake at night, and I am not particularly paranoid about it. But I find that working towards answering this question is a fun frame from which to learn about electronics, radio communications, and networking.
Since this appears to be something that is causing you some anxiety, I think it is better if I start by giving you some reassurance in that I have not yet managed to prove that any electronic device is spying on me via a hidden chip. I don’t think it is worth being paranoid about this.
I can explain some things that could be done to test whether a Linux computer spying. I am not suggesting that you try any of this. I am explaining this to you so that you can get some reassurance in the fact that, if devices were spying on us in this manner, it is likely that someone would have noticed by now.
The “spy” chip needs some way to communicate. One way a chip might communicate is via radio waves. So, the first step would be to remove the WiFi and Bluetooth dongles and any other pieces of hardware that may emit radio waves during normal operation. There is a tool called a “Spectrum Analyzer” that can be used to capture the presence of specific radio frequencies. These devices are now relatively affordable, like the tinySA, which can measure the presence of radio frequencies of up to 6 GHz.
One can make a Faraday cage, for example, by wrapping the PC with a copper-nickel coated polyester fabric to isolate the PC from the radio waves that are coming from the environment. The spectrum analyzer antennas can be placed right next to the PC and the device is left to measure continuously over several days. A script can monitor the output and keep a record of any RF signals.
Since phones are small, it is even easier to wrap them in the copper-nickel polyester fabric alongside with the spectrum analyzer antenna to check whether they emit any RF when they are off or in airplane mode with the WiFi and Bluetooth turned off.
What this experiment may allow you to conclude is that the spy chip is not communicating frequently with the external world via radio frequencies, at least not with frequencies <= 6 GHz.
Using frequencies higher 6 GHz for a low-power chip is not going be an effective method of transmitting a signal very far away. The chip could remain hidden and only emit the signal under certain rare conditions, or in response to a trigger. We can’t rule that out with this experiment, but it is unlikely.
A next step would be to test a wired connection. It could be that the spy chip can transmit the data over the internet. One can place a VPN Gateway in between their PC and the router, and use that gateway to route all the traffic to their own server using WireGuard. All network packets that leave through the PC’s ethernet connection can be captured and examined this way using Wireshark or tcpdump.
If one can show that the device is not secretly communicating via RF nor via the internet, I think it is unlikely that the device is spying on them.


You can take a lot of control by using search commands. Here is a list of commands for Google, for example: https://www.lifewire.com/advanced-google-search-3482174
By using commands like these you can narrow down your searches to the point that the impact of SEO is small. You give a much greater weight to the conditions that you have chosen.
It can be a bit of work to write a good search query, but the database that search engines search through is massive, so it makes sense that it would take some work to do this right.


Search engines like google aggregate data from multiple sites. I may want to download a datasheet for an electronic component, find an answer to a technical question, find a language learning course site, or look for museums in my area.
Usually I make specific searches with very specific conditions, so I tend to get few and relevant results. I think search engines have their place.


Fair enough. I just looked it up and if the scale in this image is correct, I agree that the size of the hole looks small in comparison. I also looked at the security video of the crash itself and it is frustrating how little we can see from it.
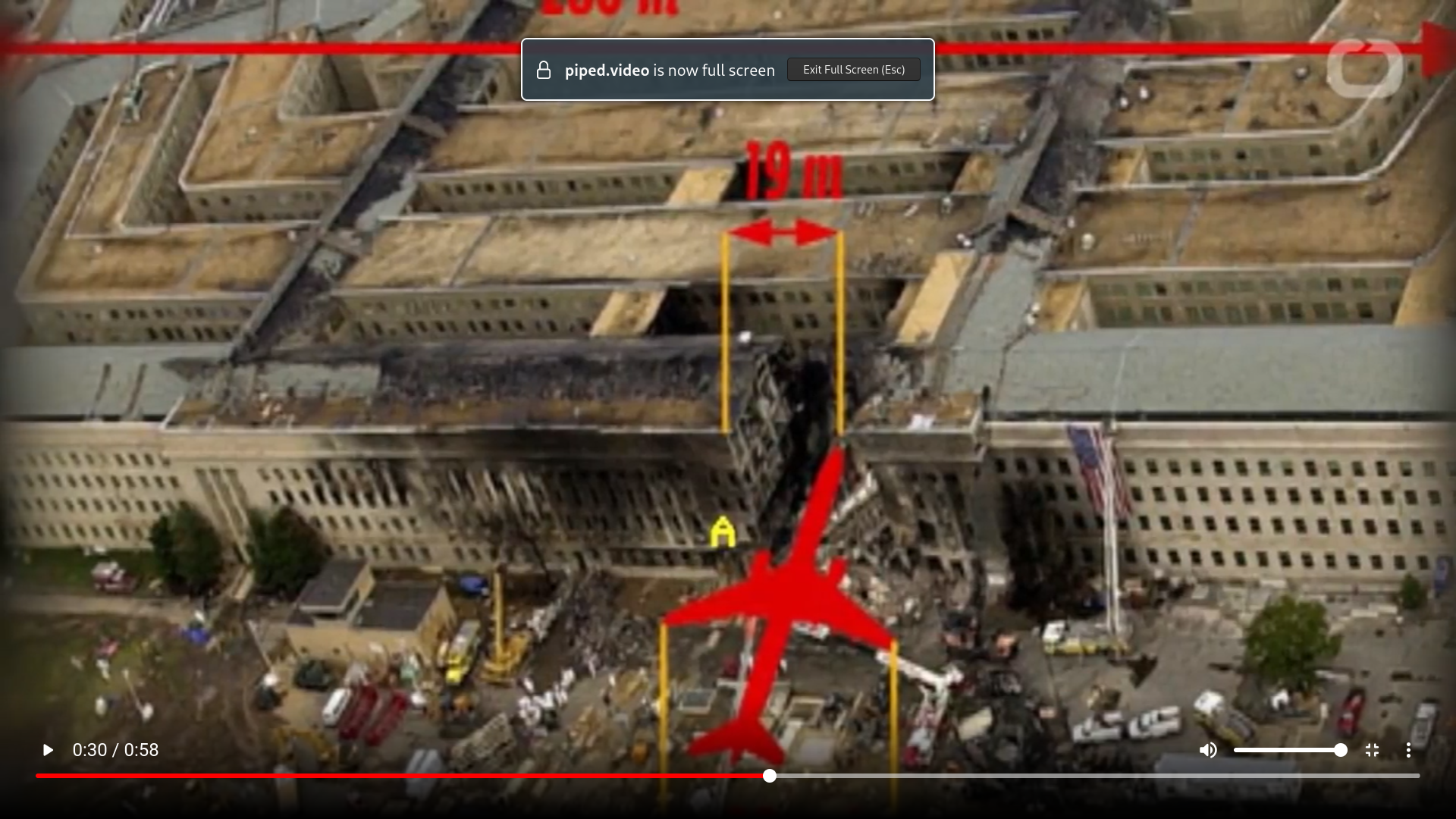
Since this was such an important event and there seems to be a lack of specific pieces of essential evidence - either because of bad luck or because of a cover-up - I understand the skepticism. And I am not a fan of blindly believing any official narrative. But, without any context, if I see that photo and someone tells me that a plane crashed into that building, I would find it probable simply because the shape is so similar to the photo of the Bijlmer accident that I’m familiar with. A plane crash seems to me like a very chaotic process, so I don’t have a good expectation of what the damage should look like.
Maybe I’ll look for a pentagon crash documentary some time.


I don’t have much of an opinion on this topic, I haven’t really looked into it.
But as soon as I saw this image, the El Al Flight 1862 which crashed in the Bijlmer in Amsterdam in 1992 immediately came to mind. The shape of the hole is very similar!
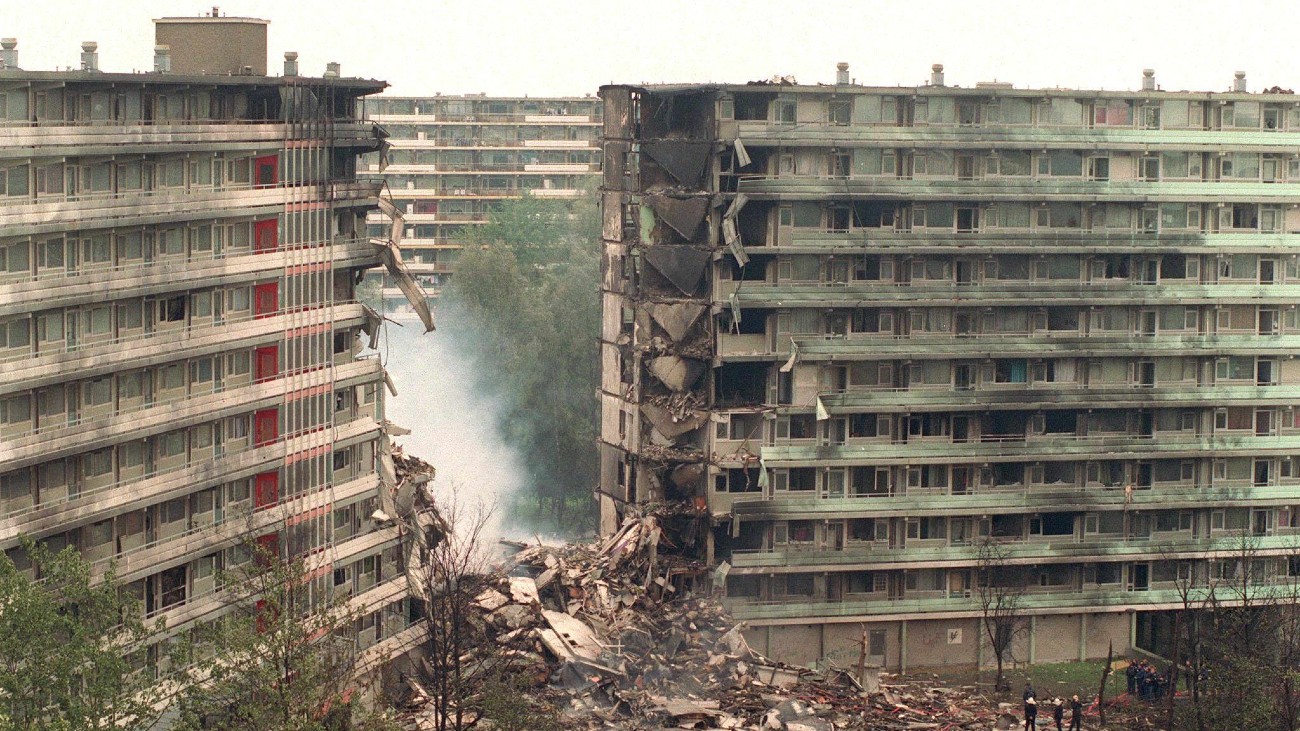

This image shows the likely position of the Bijlmer plane during the crash:

The image you posted of the Pentagon seems to me consistent with what I have seen of the Bijlmer accident, and so the shape of the hole and the absence of wings in the photo does not persuade me personally that no plane was involved.
Is the fact that I recognize this comment evidence that I use Lemmy a bit too much? 😅
I will also pay close attention and see if I can catch that happening.
I think we might see one or more “trusted fediverse” groups emerge in the next few years, with instance admins making commitments to security controls, moderation, code of conduct, etc.
There is now at least one system in place for admins to vouch for other instances being non-malicious, and to report suspected instances. It is called the fediseer: https://gui.fediseer.com/
Do you see a random nickname from a stranger, or a nickname of an account that was previously logged into using the same computer?
What is an open account sharing channel?
You can set up a personalized RSS feed with Feeder. It will take a bit of effort to set up, but you can create a feed that is very well tailored to your interests. You can get news feeds but also subscribe to other kinds of content, like scientific publications and financial statements.


I have the Tianje MF903 (https://nl.aliexpress.com/item/32719535459.html), which I bought early 2022.
But just now I have done a search and I see many more pocket wifi routers now. Unfortunately I can’t tell you if they work well, or if it is also possible to change their IMEI easily. The one I have is functional, but it doesn’t have a very long battery life.


And the audacity to talk about metadata when Telegram accounts still require a phone number today (as they did five years ago when this post was written) is just… 🤯
Not only that, but I believe that they actively try to prevent VoIP numbers from being used to create accounts.


Almost all countries require official authentication to activate a SIM card.
Fortunately not in the Netherlands. I don’t think that’s the case in the rest of the EU. I can use free sim cards as much as I want!
When communicating with cell towers, a phone will also broadcast its unique IMEI identifier. So, even if you swap the SIM card every day, your IMEI is still being broadcast the same.
Changing the IMEI of a phone in the EU is illegal, unless the manufacturer consents: https://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/2002/31/section/1
So… I have a Chinese 4G mobile router, and the manufacturer gives me the permission to change the IMEI as it is an integrated feature of the device. I use that for my data. The data codes I purchase small quantities in bulk with cash, and I can access the router via its ip from my phone’s browser to send the SMS messages to activate the data codes as needed. Since WiFi connections are abundant around here I keep these codes for emergencies. I can go a few months some time without activating data codes. I mostly use them when traveling internationally.
Thank you being around, bringing this nice community here, and helping with the federation!! 😁