

Depends on what he means by “ultra-processed”, but you can bet that it’s probably not a reasonable criteria that he’ll be using.
The man isn’t rational, and doesn’t base his conclusions on sound reasoning.
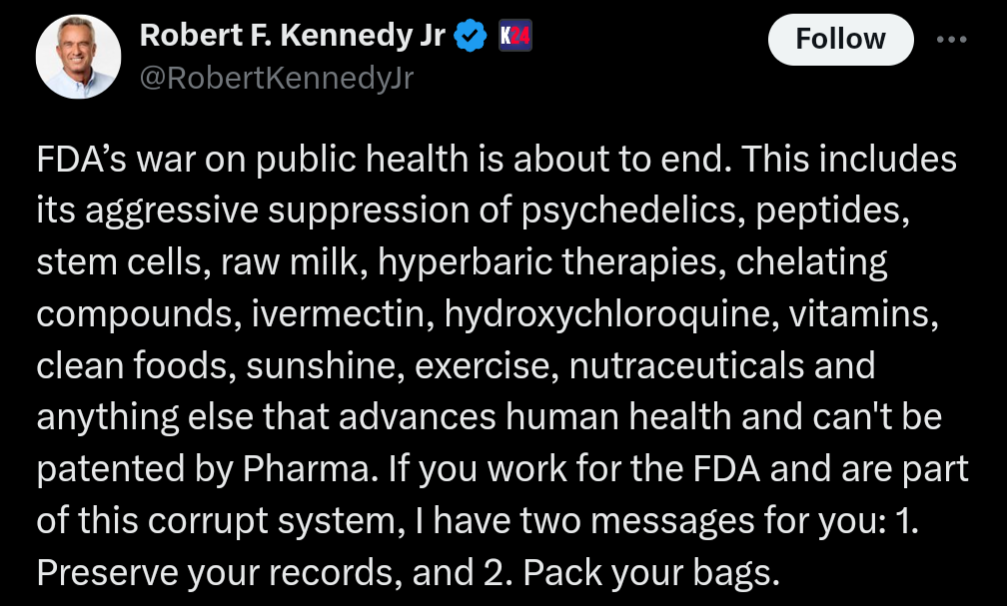
Note the call to lessen regulations around “raw milk, chelating compounds, ivermectin, hydroxychloroquine”. That’s pretty insane.
And I can almost be certain that what they’ll do is eliminate funding for snap benefits and school lunches going to what they’ll classify as “ultra processed foods”, without adjusting funding to account for what they left behind being significantly more expensive. Some definitions of “ultra-processed” include things like “store bought bread”, “frozen meals”, “soup concentrate”, “yoghurt” and “sausage”.
Call me cynical, but I think if you apply the stricter work requirements for benefits they always want, while reducing the scope of the benefits to cover fewer things, and almost nothing helpful for the people with the severe time restrictions the work requirements can cause you’ll end up seeing people use the benefits far less often, because they give less usable food for the money. Then they’ll use that to justify reducing the size of the program even further.
We expect people making school lunches to make hundreds of meals that finish at the same time, to have the meal be nutritionally complete, tasty, and now also not use frozen or premade ingredients. We give them literally $1 for the ingredients for these meals, and maybe another $2 for operational overhead like labor costs and equipment.
Saying you can’t use canned tomato sauce, peanut butter, pre-packaged bread or ground meats is basically just cutting funding for feeding children under the guise of not paying for a scary sounding classification of food.






He kept his two income streams tied together, so that when one ran into trouble it took the other one down with it. He could have just as easily kept the business separate and potentially been able to keep one of the income streams working when the shit hit the fan.